Resources
Resources

Generative AI
Evaluatorq: An Open-Source Framework for GenAI Evaluations
Evaluatorq is an open-source framework for reliably testing GenAI systems. It helps teams catch regressions caused by prompt, model, or parameter changes by defining jobs, running parallel evaluators, and testing against datasets acting as the regression testing layer for LLM workflows.
January 12, 2026

Ewa Szyszka
DevRel Engineer
Key Takeaways
Evaluatorq is an open-source TypeScript and Python framework for building reproducible GenAI evaluations.
Run evaluations locally or in CI/CD pipelines using jobs, evaluators, and datasets as first-class building blocks.
Connect to Orq datasets with an API key to share evaluation data, visualize results, and track model quality over time.
Bring LLM-powered apps from prototype to production
Discover a collaborative platform where teams work side-by-side to deliver LLM apps safely.
Bring LLM-powered apps from prototype to production
Discover a collaborative platform where teams work side-by-side to deliver LLM apps safely.
You’ve seen the potential of large language models (LLMs) and other GenAI systems, but they’re highly unpredictable. Small changes in prompt, model versions, or parameters can lead to very different outputs. Sometimes, this introduces subtle regressions that aren’t easy to catch and only become apparent until they affect end users. This is where Evaluatorq comes in.
What is Evaluatorq?
Evaluatorq is our new open-source Python and TypeScript framework for building and running GenAI evaluations. It gives developers a simple, type-safe way to:
Define jobs: These are functions that run your model over inputs and produce outputs.
Set up parallel evaluators: Evaluators are scoring functions that check whether outputs meet expectations (e.g. LLM-as-a-judge), with Evaluatorq you can run multiple evals simultaneously
Flexible Data Sources: Apply jobs and evaluators over datasets. These could be inline arrays, async sources, or even datasets managed in the Orq.ai platform.
Automate at scale: Discover and execute all evaluation files with a CLI.
Invoke preconfigured deployments on the platform
These components are designed to feelfamiliar to developers - jobs resemble test cases, evaluators act as assertions, and datasets provide the test inputs.
Use Cases
Evaluatorq is designed to fit a wide range of LLM and multimodal evaluation workflows. By defining custom jobs and evaluators, teams can adapt it to any scenario:
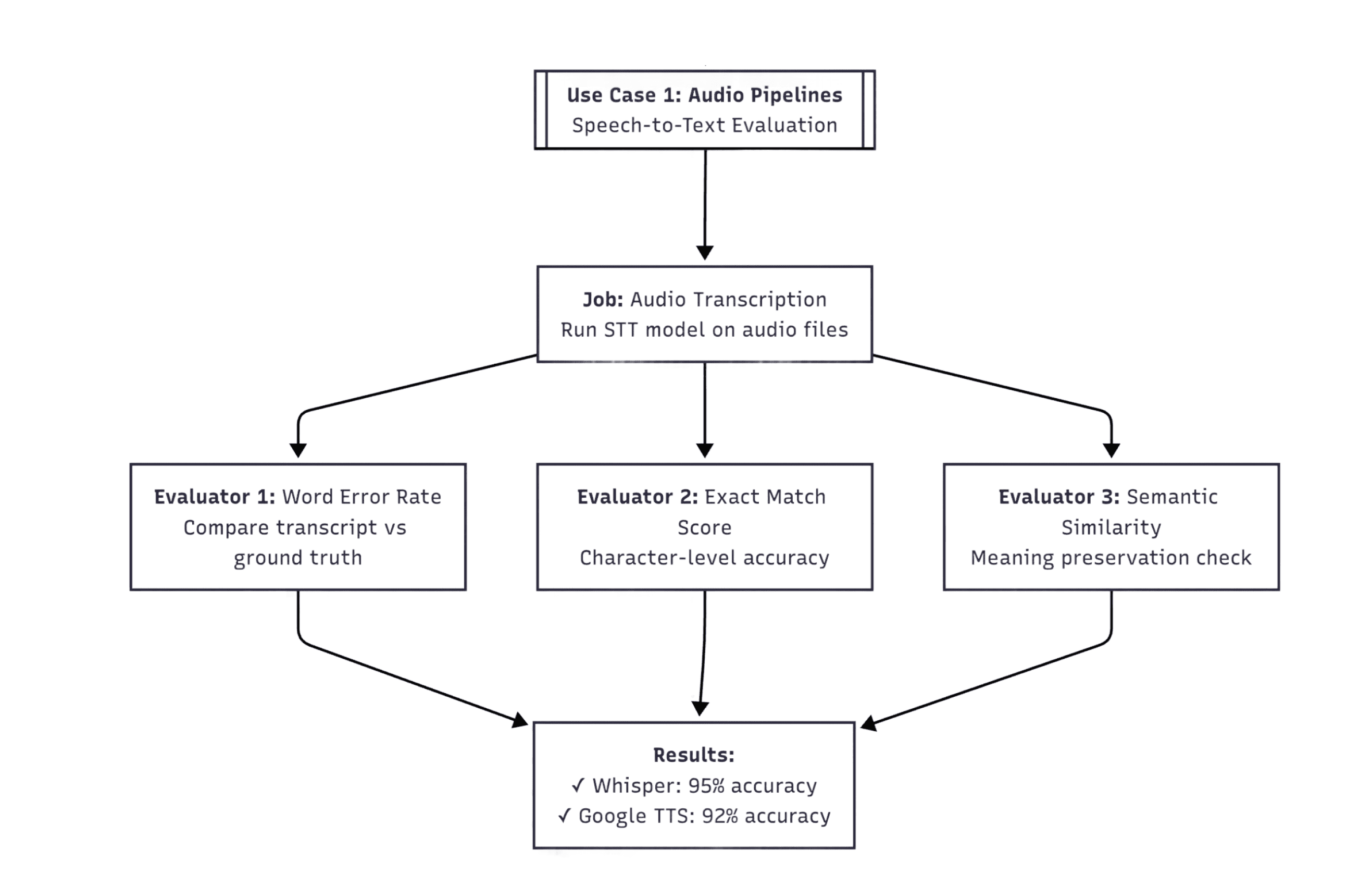
1. Speech-to-text quality in Audio Pipelines
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing speech-to-text accuracy against reference transcripts. For instance, you can compare two STT models (e.g. Whisper and Google Speech-to-Text) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator for fluency assessment to measure word error rate, semantic accuracy, and transcript completeness in parallel - which is critical for validating medical and legal transcription systems where accuracy directly impacts patient care and legal outcomes.
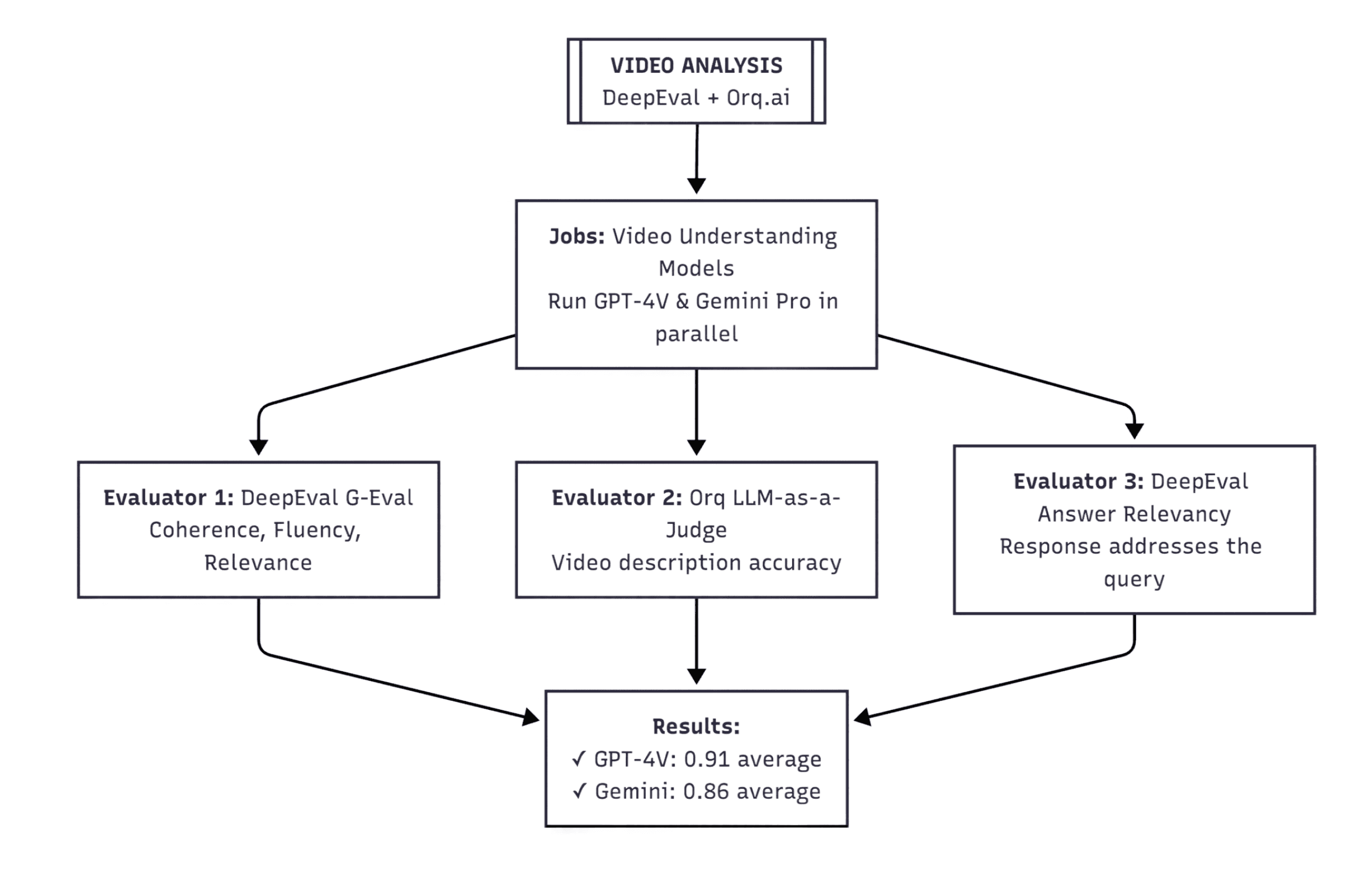
2. Video captioning analysis
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing video captioning against expected responses. For instance, you can compare two multimodal vision models (e.g. GPT-4V and Gemini Pro) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator and bring third-party evaluators (e.g. DeepEval) to assess coherence, semantic overlap and answer relevancy in parallel.
These are just some starting points. Since jobs and evaluators are arbitrary functions, you can extend Evaluatorq to any custom pipeline, where it’s an agent workflow or a proprietary model.
How it Works
Evaluatorq evaluations follow a simple sequence: install the package, define a job, create an evaluator, and run everything over a dataset.
Step 1: Install
Add Evaluatorq to your project. You can find full installation guide here
npm i @orq-ai/evaluatorq |
Step 2: Define a Job
A job defines the model task you want to evaluate. It takes inputs and returns outputs.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
Step 3: Create an Evaluator
You can start with inline examples.
Here, we add a length-check evaluator directly in the evaluation.
await evaluatorq("text-analysis", { |
Step 4: Run Against an Orq Dataset
Instead of inline examples, you can connect to a dataset stored in Orq.ai. This makes it easy to share consistent evaluation data across your team.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
If you set the ORQ_API_KEY environment variable, results are automatically uploaded to Orq.ai, where they can be visualized and compared with past runs.
Bringing Reliable Evals to Your GenAI Workflows
Evaluations are the regression tests of machine learning. Without them, it’s tough to track model quality, catch regressions, or scale AI workflows with confidence.
Evaluatorq makes this process simple and easy.
It combines building blocks like jobs and datasets to let you:
Evaluate everything from text analysis to multimodal pipelines
Integrate results into CI/CD
Keep performance under control as your system evolves
Whether you’re running quick local checks or coordinating team-wide evaluations in the Orq platform, Evaluatorq provides your team with a reproducible framework for testing and improving LLM workflows.
You’ve seen the potential of large language models (LLMs) and other GenAI systems, but they’re highly unpredictable. Small changes in prompt, model versions, or parameters can lead to very different outputs. Sometimes, this introduces subtle regressions that aren’t easy to catch and only become apparent until they affect end users. This is where Evaluatorq comes in.
What is Evaluatorq?
Evaluatorq is our new open-source Python and TypeScript framework for building and running GenAI evaluations. It gives developers a simple, type-safe way to:
Define jobs: These are functions that run your model over inputs and produce outputs.
Set up parallel evaluators: Evaluators are scoring functions that check whether outputs meet expectations (e.g. LLM-as-a-judge), with Evaluatorq you can run multiple evals simultaneously
Flexible Data Sources: Apply jobs and evaluators over datasets. These could be inline arrays, async sources, or even datasets managed in the Orq.ai platform.
Automate at scale: Discover and execute all evaluation files with a CLI.
Invoke preconfigured deployments on the platform
These components are designed to feelfamiliar to developers - jobs resemble test cases, evaluators act as assertions, and datasets provide the test inputs.
Use Cases
Evaluatorq is designed to fit a wide range of LLM and multimodal evaluation workflows. By defining custom jobs and evaluators, teams can adapt it to any scenario:
1. Speech-to-text quality in Audio Pipelines
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing speech-to-text accuracy against reference transcripts. For instance, you can compare two STT models (e.g. Whisper and Google Speech-to-Text) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator for fluency assessment to measure word error rate, semantic accuracy, and transcript completeness in parallel - which is critical for validating medical and legal transcription systems where accuracy directly impacts patient care and legal outcomes.

2. Video captioning analysis
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing video captioning against expected responses. For instance, you can compare two multimodal vision models (e.g. GPT-4V and Gemini Pro) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator and bring third-party evaluators (e.g. DeepEval) to assess coherence, semantic overlap and answer relevancy in parallel.

These are just some starting points. Since jobs and evaluators are arbitrary functions, you can extend Evaluatorq to any custom pipeline, where it’s an agent workflow or a proprietary model.
How it Works
Evaluatorq evaluations follow a simple sequence: install the package, define a job, create an evaluator, and run everything over a dataset.
Step 1: Install
Add Evaluatorq to your project. You can find full installation guide here
npm i @orq-ai/evaluatorq |
Step 2: Define a Job
A job defines the model task you want to evaluate. It takes inputs and returns outputs.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
Step 3: Create an Evaluator
You can start with inline examples.
Here, we add a length-check evaluator directly in the evaluation.
await evaluatorq("text-analysis", { |
Step 4: Run Against an Orq Dataset
Instead of inline examples, you can connect to a dataset stored in Orq.ai. This makes it easy to share consistent evaluation data across your team.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
If you set the ORQ_API_KEY environment variable, results are automatically uploaded to Orq.ai, where they can be visualized and compared with past runs.
Bringing Reliable Evals to Your GenAI Workflows
Evaluations are the regression tests of machine learning. Without them, it’s tough to track model quality, catch regressions, or scale AI workflows with confidence.
Evaluatorq makes this process simple and easy.
It combines building blocks like jobs and datasets to let you:
Evaluate everything from text analysis to multimodal pipelines
Integrate results into CI/CD
Keep performance under control as your system evolves
Whether you’re running quick local checks or coordinating team-wide evaluations in the Orq platform, Evaluatorq provides your team with a reproducible framework for testing and improving LLM workflows.
You’ve seen the potential of large language models (LLMs) and other GenAI systems, but they’re highly unpredictable. Small changes in prompt, model versions, or parameters can lead to very different outputs. Sometimes, this introduces subtle regressions that aren’t easy to catch and only become apparent until they affect end users. This is where Evaluatorq comes in.
What is Evaluatorq?
Evaluatorq is our new open-source Python and TypeScript framework for building and running GenAI evaluations. It gives developers a simple, type-safe way to:
Define jobs: These are functions that run your model over inputs and produce outputs.
Set up parallel evaluators: Evaluators are scoring functions that check whether outputs meet expectations (e.g. LLM-as-a-judge), with Evaluatorq you can run multiple evals simultaneously
Flexible Data Sources: Apply jobs and evaluators over datasets. These could be inline arrays, async sources, or even datasets managed in the Orq.ai platform.
Automate at scale: Discover and execute all evaluation files with a CLI.
Invoke preconfigured deployments on the platform
These components are designed to feelfamiliar to developers - jobs resemble test cases, evaluators act as assertions, and datasets provide the test inputs.
Use Cases
Evaluatorq is designed to fit a wide range of LLM and multimodal evaluation workflows. By defining custom jobs and evaluators, teams can adapt it to any scenario:
1. Speech-to-text quality in Audio Pipelines
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing speech-to-text accuracy against reference transcripts. For instance, you can compare two STT models (e.g. Whisper and Google Speech-to-Text) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator for fluency assessment to measure word error rate, semantic accuracy, and transcript completeness in parallel - which is critical for validating medical and legal transcription systems where accuracy directly impacts patient care and legal outcomes.

2. Video captioning analysis
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing video captioning against expected responses. For instance, you can compare two multimodal vision models (e.g. GPT-4V and Gemini Pro) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator and bring third-party evaluators (e.g. DeepEval) to assess coherence, semantic overlap and answer relevancy in parallel.

These are just some starting points. Since jobs and evaluators are arbitrary functions, you can extend Evaluatorq to any custom pipeline, where it’s an agent workflow or a proprietary model.
How it Works
Evaluatorq evaluations follow a simple sequence: install the package, define a job, create an evaluator, and run everything over a dataset.
Step 1: Install
Add Evaluatorq to your project. You can find full installation guide here
npm i @orq-ai/evaluatorq |
Step 2: Define a Job
A job defines the model task you want to evaluate. It takes inputs and returns outputs.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
Step 3: Create an Evaluator
You can start with inline examples.
Here, we add a length-check evaluator directly in the evaluation.
await evaluatorq("text-analysis", { |
Step 4: Run Against an Orq Dataset
Instead of inline examples, you can connect to a dataset stored in Orq.ai. This makes it easy to share consistent evaluation data across your team.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
If you set the ORQ_API_KEY environment variable, results are automatically uploaded to Orq.ai, where they can be visualized and compared with past runs.
Bringing Reliable Evals to Your GenAI Workflows
Evaluations are the regression tests of machine learning. Without them, it’s tough to track model quality, catch regressions, or scale AI workflows with confidence.
Evaluatorq makes this process simple and easy.
It combines building blocks like jobs and datasets to let you:
Evaluate everything from text analysis to multimodal pipelines
Integrate results into CI/CD
Keep performance under control as your system evolves
Whether you’re running quick local checks or coordinating team-wide evaluations in the Orq platform, Evaluatorq provides your team with a reproducible framework for testing and improving LLM workflows.
You’ve seen the potential of large language models (LLMs) and other GenAI systems, but they’re highly unpredictable. Small changes in prompt, model versions, or parameters can lead to very different outputs. Sometimes, this introduces subtle regressions that aren’t easy to catch and only become apparent until they affect end users. This is where Evaluatorq comes in.
What is Evaluatorq?
Evaluatorq is our new open-source Python and TypeScript framework for building and running GenAI evaluations. It gives developers a simple, type-safe way to:
Define jobs: These are functions that run your model over inputs and produce outputs.
Set up parallel evaluators: Evaluators are scoring functions that check whether outputs meet expectations (e.g. LLM-as-a-judge), with Evaluatorq you can run multiple evals simultaneously
Flexible Data Sources: Apply jobs and evaluators over datasets. These could be inline arrays, async sources, or even datasets managed in the Orq.ai platform.
Automate at scale: Discover and execute all evaluation files with a CLI.
Invoke preconfigured deployments on the platform
These components are designed to feelfamiliar to developers - jobs resemble test cases, evaluators act as assertions, and datasets provide the test inputs.
Use Cases
Evaluatorq is designed to fit a wide range of LLM and multimodal evaluation workflows. By defining custom jobs and evaluators, teams can adapt it to any scenario:
1. Speech-to-text quality in Audio Pipelines
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing speech-to-text accuracy against reference transcripts. For instance, you can compare two STT models (e.g. Whisper and Google Speech-to-Text) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator for fluency assessment to measure word error rate, semantic accuracy, and transcript completeness in parallel - which is critical for validating medical and legal transcription systems where accuracy directly impacts patient care and legal outcomes.

2. Video captioning analysis
Another use-case of Evaluatorq is testing video captioning against expected responses. For instance, you can compare two multimodal vision models (e.g. GPT-4V and Gemini Pro) with a built-in Orq.ai LLM-as-a-judge evaluator and bring third-party evaluators (e.g. DeepEval) to assess coherence, semantic overlap and answer relevancy in parallel.

These are just some starting points. Since jobs and evaluators are arbitrary functions, you can extend Evaluatorq to any custom pipeline, where it’s an agent workflow or a proprietary model.
How it Works
Evaluatorq evaluations follow a simple sequence: install the package, define a job, create an evaluator, and run everything over a dataset.
Step 1: Install
Add Evaluatorq to your project. You can find full installation guide here
npm i @orq-ai/evaluatorq |
Step 2: Define a Job
A job defines the model task you want to evaluate. It takes inputs and returns outputs.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
Step 3: Create an Evaluator
You can start with inline examples.
Here, we add a length-check evaluator directly in the evaluation.
await evaluatorq("text-analysis", { |
Step 4: Run Against an Orq Dataset
Instead of inline examples, you can connect to a dataset stored in Orq.ai. This makes it easy to share consistent evaluation data across your team.
import { evaluatorq, job } from "@orq-ai/evaluatorq"; |
If you set the ORQ_API_KEY environment variable, results are automatically uploaded to Orq.ai, where they can be visualized and compared with past runs.
Bringing Reliable Evals to Your GenAI Workflows
Evaluations are the regression tests of machine learning. Without them, it’s tough to track model quality, catch regressions, or scale AI workflows with confidence.
Evaluatorq makes this process simple and easy.
It combines building blocks like jobs and datasets to let you:
Evaluate everything from text analysis to multimodal pipelines
Integrate results into CI/CD
Keep performance under control as your system evolves
Whether you’re running quick local checks or coordinating team-wide evaluations in the Orq platform, Evaluatorq provides your team with a reproducible framework for testing and improving LLM workflows.
FAQ
Can I use Evaluatorq with any model or framework?
Do I need to use the Orq.ai platform to run Evaluatorq?

About
Ewa Szyszka is a Developer Relations Engineer at Orq.ai who's spent her career bridging the gap between cutting-edge AI research and the developers building with it. With a background in NLP R&D that's taken her from San Francisco to Tokyo, at Orq.ai her mission is translating the latest GenAI trends into workflows that actually work in production.

About
Ewa Szyszka is a Developer Relations Engineer at Orq.ai who's spent her career bridging the gap between cutting-edge AI research and the developers building with it. With a background in NLP R&D that's taken her from San Francisco to Tokyo, at Orq.ai her mission is translating the latest GenAI trends into workflows that actually work in production.

About
Ewa Szyszka is a Developer Relations Engineer at Orq.ai who's spent her career bridging the gap between cutting-edge AI research and the developers building with it. With a background in NLP R&D that's taken her from San Francisco to Tokyo, at Orq.ai her mission is translating the latest GenAI trends into workflows that actually work in production.

About
Ewa Szyszka is a Developer Relations Engineer at Orq.ai who's spent her career bridging the gap between cutting-edge AI research and the developers building with it. With a background in NLP R&D that's taken her from San Francisco to Tokyo, at Orq.ai her mission is translating the latest GenAI trends into workflows that actually work in production.







